
Introduction
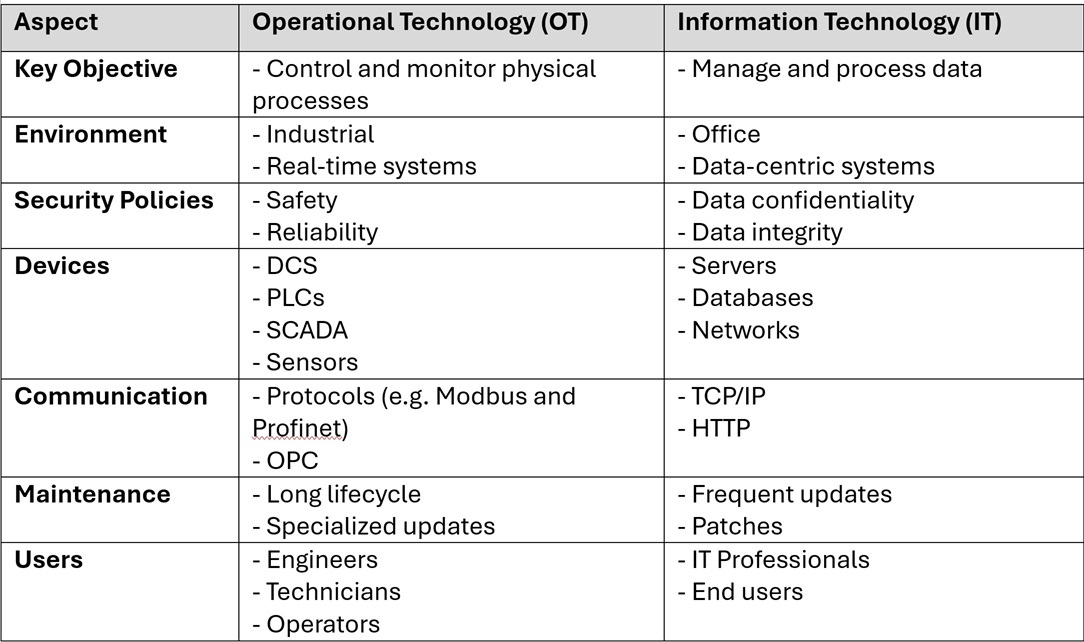
Dashboards are used both in IT and OT (Operational Technology) domains and across all industries. They have become commonplace and for many are a critical productivity tool. We’ll discuss why and explore them through a couple of case study examples that showcase what they can offer and why they are such a valuable digital solution for many roles within an organisation.
Why the need?
Dashboards can be effective productivity enhancement tool. If designed well, this information that can be easily accessed to make data-driven decisions swiftly and accurately.
A common way to capture and present the information is in the form of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). KPIs are a quantifiable measure of performance over time for a specific objective. Information captured in this way allows users, teams, and the wider stakeholder audience to gauge progress, assess performance against set targets and gain useful insights to make better decisions.
Standardised KPIs across the organisation enable performance benchmarking that allow comparisons to be made across sites, regions, or even globally (if applicable). These comparisons allow for the sharing of best practices through Centres of Excellence (CoE) or at company and industry events that provide an opportunity to share learnings and proven methods for repeatable success.
Reduced Manual Processing
For some organisations, source data would typically live in a variety of different data sources. This could be in spreadsheets, databases, and from different IT and OT systems. This would then have to be carried out each time for each reporting frequency. If this data capture can be automated, this will greatly improve operational efficiency.
Improved Data Accuracy
As well as it being a time-consuming activity, manual processing of data which may include data aggregation and custom calculations, can be prone to errors. Data automation will also have the potential to increase data accuracy. Important steps in this activity are that data quality reviewed and improved and ‘single version of the truth’ source data.
Faster Decision-Making
Having the right information immediately available is a big productivity boost. If there is a time lag between when the data is required and when it can be made available, then decisions are then made with old data and opportunities are potentially missed. The high availability of data increases an organisations agility and provide a competitive edge.
Operational and Strategic Benefits
Dashboards offer both operational and strategic benefits. This list is not exhaustive but provides an insight into some of the benefits that can be achieved:
- Freeing up of valuable resources to work on other high value resources
- Greater speed and simplicity in the sourcing and data preparation
- The data can become available to a wider audience
- Trends can be observed over specific and longer periods of time
- The data can be used in predictive analytics and forecasting models
- The data can be leveraged for Machine Learning (ML) and AI initiatives
Case Study Examples
1 - Operational
From an operational standpoint, dashboards can serve host of different purposes such as performance monitoring, inventory management, to production optimisation. This list is by no means exhaustive but gives some insight into some different use cases:
- Performance Management
- Inventory Monitoring
- Reliability and Maintenance
- Trends that signify operational degradation
- Events and threshold alerts
Let’s use an Offshore Gas or Oil Production Platform as an example. Depending upon the operational user role, here are some operational KPIs that could feature on a dashboard:
- Production rates/volums vs production targets - will inform us if we are on track to meet production targets
- Safety summary - provide and track key safety related event information
- Chemicals inventory - ensure there are enough chemical injection fluids for corrosion monitoring for example and to manage ordering and re-supply
- Emissions monitoring - track and ensure environmental compliance and targets are being met
- Event monitoring - summarise key operational events or alarms
2 - Retail
Dashboards provide a good opportunity to capture metrics that can be used to track retail performance, quickly identify areas of concern that indeed may have a simple explanation or may require a deeper investigation to understand the root cause.
The metrics tracked by a dashboard will vary depending on the specific performance objectives and use cases within retail.
If we take a retail store as an example:
- Sales metrics - allows review of monthly, quarterly and year-to-date sales data
- Customer centric data - track customer satisfaction levels and feedback
- Personnel data - to track staff utlisation to optimise resource allocation
- Safety data - capture and track safety performance data to ensure HSE standards are being met and identify additional training requirements
- Mobile platform version - allows visiting retail managers to access key data remotely
A dashboard can also enable performance to be evaluated for sites regionally, nationally and globally if applicable. Capturing KPI data in this way also allows for benchmarking and the sharing of best practices both externally and within an organisation.
Dashboard Solution Challenges
Delivery
For many dashboard implementation projects, starting small (e.g. with a Pilot or Minimum Viable Product - MVP) helps to minimise risk and feed learnings into the next development iteration. Adopting an agile approach will provide a methodology where functionality with the highest business value is prioritised in the product backlog. An iterative feedback loop will allow learnings to be incorporated into future iterations, contributing to a successful delivery, and long-term success.
Data management plays a key part in an organisation to develop and deploy a solution that contains high quality data, data feeds (including any data processing required – e.g., Extraction Transforming and Loading of data) and a highly responsive solution that can be used on a variety of platforms. The topic of data management is covered in more detail in a white paper that can be shared upon request.
User Experience (UX) is an important part of delivering a solution that will have a high user adoption rate. Some delivery teams will have dedicated UX specialist(s) to ensure that is important requirement is met.
There are many choices available in choosing the dashboard solution, this could be using a BI solution or developing a custom dashboard. Factors that will have a bearing are things like a strategic roadmap (if there is one - it will help with ensuring a forward looking technology alignment), business requirements, and system integration considerations.
Data security is a critical consideration. With the ever-increasing amount of cybersecurity threats, this will feature heavily in the solution design. Cloud-based Master Data Management, advanced encryption technology, zero trust architectural principles may all be part of the solution design and wider enterprise architectural landscape.
Ensuring solution effectiveness
There needs to be some strategic thought as to what dashboards are to be created and the intended audience. Hence the requirements capture and having a business case that clearly demonstrates the value creation are two important activities. User Acceptance Testing which can provide valuable early feedback and User Training are also key activities to ensure value creation.
Accessibility of the solution needs to be factored into the design considerations. The user base may include remote support teams as well as onsite users who may require mobile or field devices to access the dashboard. Therefore, compatibility with different operating systems and formats will also have to be part of the delivery scope.
A big danger and something that can happen in organisations that there are many dashboards created (e.g. typically through siloed behaviour due to a lack of strategic thought and a lack of internal communication) and so the latest dashboard just becomes another solution for the user base to use. The danger in this instance is that some users then have too many tools at their disposal which can have a negative impact on their productivity.
Periodic reviews of existing dashboards, incorporating user feedback (e.g. surveys), should be conducted to ensure ongoing relevance. These reviews serve to help with the developments of future versions and ensure operational optimisation.
A recommendation to ensure effectiveness, is that best practices should be put in place by way of having dashboard standardisation frameworks and implementing a governance board.
Conclusion
Dashboards are essential tools in boosting productivity. If designed effectively, they bring many benefits by helping to present the right information efficiently and effectively enabling quicker and decisive decisions to be made. This will improve workflow processes which in turn will improve operational efficiency and profitability.
Considerations in the design, business requirements, and user experience are all factors in ensuring that a dashboard is a business value creation tool that makes a tangible contribution to the organisation’s operational and Continuous Improvement initiatives.







 Remote working practices calls for the increased need for digital solutions to achieve this new modus operandi. These new ways of working were a longer-term priority for organisations prior to the pandemic and now need to be brought forward.
Remote working practices calls for the increased need for digital solutions to achieve this new modus operandi. These new ways of working were a longer-term priority for organisations prior to the pandemic and now need to be brought forward.